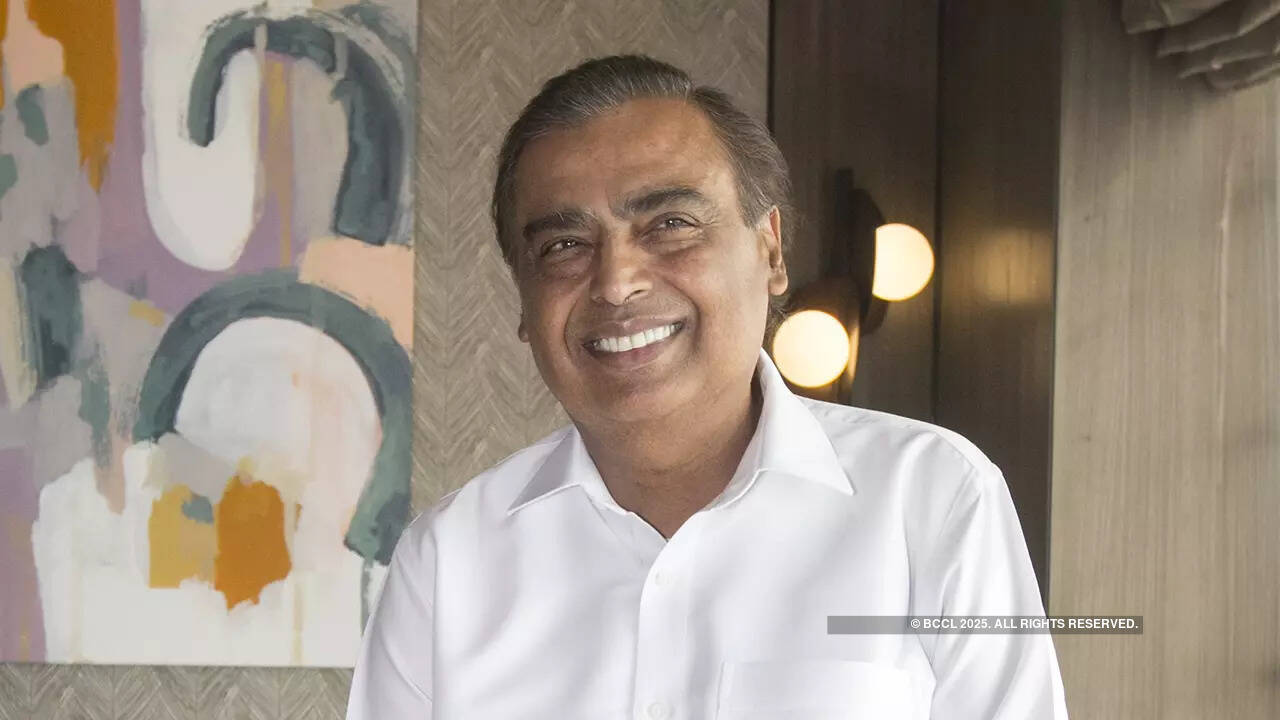
From Ottawa to Beijing, US President Donald Trump’s trade war has made many enemies. But it has also won America some allies. Asia’s richest tycoon is preparing to welcome US cargo originally meant for China but rerouted to India. The ship Mukesh Ambani is waiting for is laden with ethane.
This colorless, odorless component of natural gas is shipped in liquefied form in special carriers such as STL Qianjiang, which is currently on its way from the US Gulf Coast to billionaire Ambani’s terminal in Dahej, Gujarat, on India’s western seaboard. There, his flagship Reliance Industries Ltd. has an ethane cracker to produce ethylene, a key building block of plastic products.
The unit, completed in 2017, made Reliance “the first company to globally conceptualize large-scale imports of ethane from North America as feedstock,” it boasted in a press release back then. Eight years later, that foresight may come in handy to trade negotiators in New Delhi. “Stop obsessing over your $43 billion trade deficit with us,” they might like to tell their counterparts in Washington, as both sides try to close a deal ahead of the July 9 US deadline for 26% reciprocal tariffs. “We’re going to buy your gas.”
The 68-year-old petrochemicals czar bet on North American ethane more than a decade ago. His father Dhirubhai Ambani, the founder of the empire, was the original “Polyester Prince.” And although the son has ventured into new areas and added $57 billon in retail and digital services, the annual revenue from the legacy oils-to-chemicals business is still bigger at $74 billion.
Historically, Reliance and other refiners have cracked naphtha — obtained by distilling crude oil — to make ethylene. The conversion efficiency is low at around 30%, compared with 80% for ethane. But since crude oil had to be imported anyway to produce motor spirits, it made sense to use it for making polyester and other polymers as well. Ethane, which on an energy-equivalent basis is half as expensive as naphtha, hasn’t been popular until now. In fact, Qatar didn’t even bother to separate it from the natural gas it supplied to India. But even that is changing. Under a new agreement with India’s Oil & Natural Gas Corp., QatarEnergy will only provide “lean” gas. If the buyer wants ethane, it will have to pay for it. ONGC recently entered into a deal with Mitsui OSK Lines Ltd., which will build, own and operate two very large carriers for the state-owned firm to import ethane. Here, too, Ambani wrote the template. Reliance co-owns a fleet of six such vessels. It now wants to lay a 100-kilometer (62-mile) pipeline to bring ethane from the terminal to another of its processing units in Gujarat. New capacities for ethane cracking are coming up, too, including by GAIL India Ltd., a public-sector firm like ONGC.
It isn’t clear if this entanglement with North American feedstock will expand indefinitely. Just how much more ethane could Reliance and others handle? After all, it’s still an oil-centric economy they serve. But if the dependence grows, it could profoundly alter India’s fuel economics. For one thing, Indian state-owned refiners may become unprofitable dumping grounds for Middle Eastern crude. Any residual use for the naphtha they churn out alongside transport fuels won’t compensate for the loss of its central role in making everything from polyester and detergents to fertilizers, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals.
Oil is on extra time in India. A third of the vehicles sold last year by the nation’s largest carmaker run on compressed natural gas. To manage pollution, and reduce dependence on imported fossil fuels, New Delhi has mandated the addition of 20% bio-ethanol in gasoline. Mass adoption of electric vehicles will further cut into gasoline demand. Even then, a government-controlled firm is setting up a 9-million-ton-a-year crude refinery in the southern state of Andhra Pradesh. I suspect the reason the project is going ahead is because the state, eager to attract capital and create jobs, is offering lavish subsidies. Otherwise, the investment case is weak.
Meanwhile, Ambani plans to add three more ethane carriers to its fleet. Now that Trump has fallen out with Elon Musk, the White House may have room for a new centi-billionaire guest. Both parties may gain from a closer friendship. While the trade war with China is on pause, the fate of US ethane still hangs in limbo. Although India can’t match the much larger Chinese appetite for cracking ethane, it can certainly absorb some of the oversupply. Trump will get to brag about how his trade policies are making America great again — and his sons may get some tips on how to run their telecom startup. Ambani will fight off the pressure on his margins by shifting to a cheaper feedstock.
The tycoon runs India’s biggest telecommunications and retail networks, but it’s only now that his family has started climbing up on the list of global celebrities. First came the glitzy, five-month-long, $600-million-dollar wedding celebration last year of the youngest of the three Ambani children, the heir apparent of Reliance’s energy business. Ivanka Trump and Jared Kushner were among the attendees. Then Trump met Ambani and his wife, Nita, at his pre-inauguration party. This fall, Nita Ambani will take over New York’s Lincoln Center for a “Slice of India” weekend.
Making a mark as a big buyer of American ethane may not draw the attention of Vanity Fair. But the White House will surely take note.
(Disclaimer: The opinions expressed in this column are that of the writer. The facts and opinions expressed here do not reflect the views of www.economictimes.com.)